
Atoms and Atomic Structure
The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram - Science Struck The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram An atom is the basic unit of matter. The following article provides you with diagrams that will help you understand the structure of an atom better.
Atomic structure WGHS Junior Science
All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Approximately 50 million atoms of solid matter lined up in a row would measure 1 cm (0.4 inch). A convenient unit of length for measuring atomic sizes is the angstrom (Å), defined as 10 −10 metre. The radius of an atom measures 1-2 Å.

The Structure of the Atom GCSE Physics Science) AQA Revision Study Rocket
Relative charge. -1. The number of electrons in an atom is always the same as the number of protons, so atoms are electrically. neutral. overall. Atoms can lose or gain electrons. When they do.
What is Atom? How does it Exist? and it's Symbols Teachoo
Because of the definition of the unified atomic mass unit, each carbon-12 atom has an atomic mass of exactly 12 u, and so a mole of carbon-12 atoms weighs exactly 0.012 kg. Neils Bohr's model a.
Subatomic Makeup Of An Atom Makeupview.co
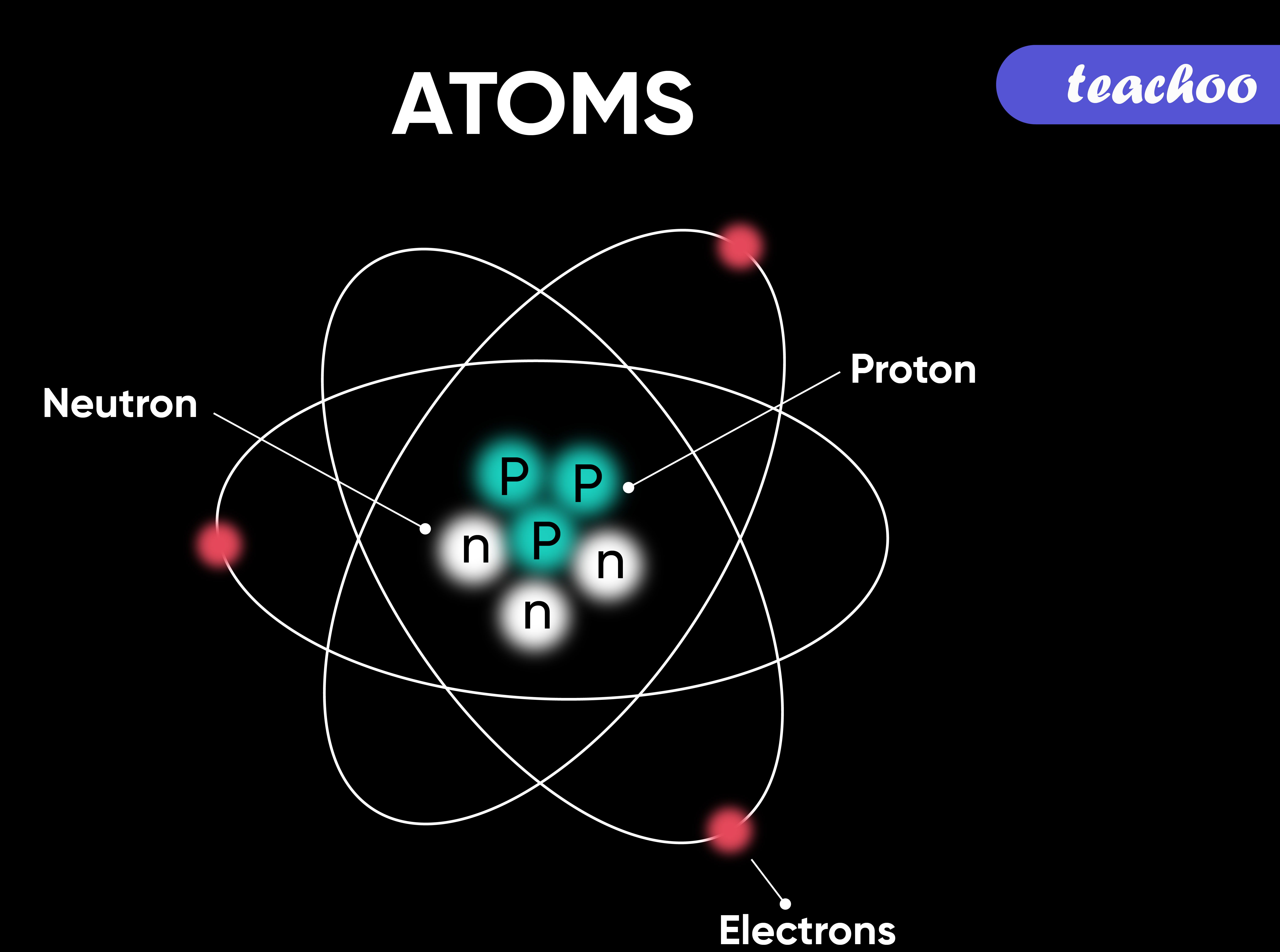
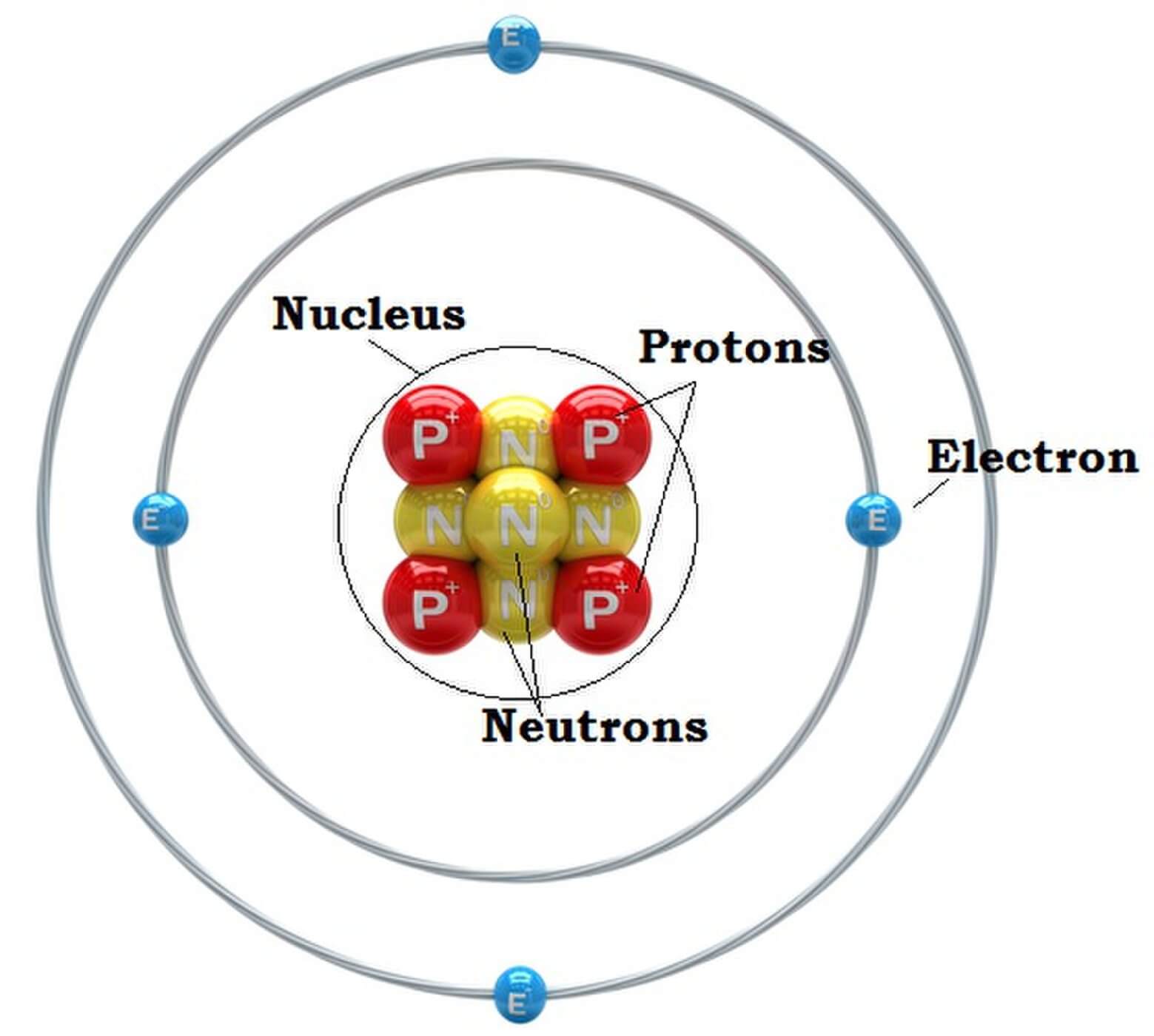
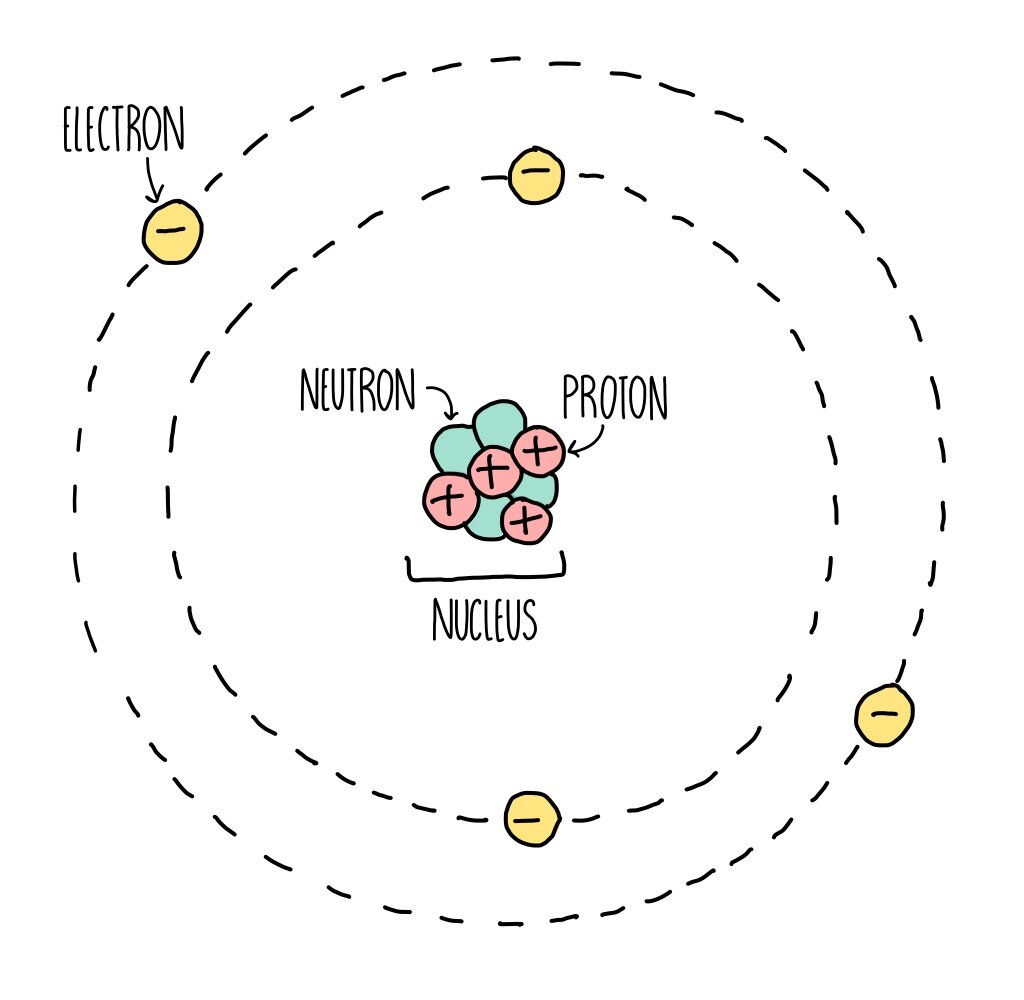
An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10 -24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic mass unit (amu.
What is an Atom? Definitions & Examples Let us learn Basics News Bugz
The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom. The next atom is the alkali metal lithium with an atomic number of 3. The first two electrons in lithium fill the 1 s orbital and have the same sets of four quantum numbers as the two electrons in helium.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
35 Label The Parts Of The Atom In The Diagram Below Labels For Your Ideas
In this video we cover the structure of atoms, what are subatomic particles, energy levels, and stable and reactive atoms.Transcript and notesAtomic structur.
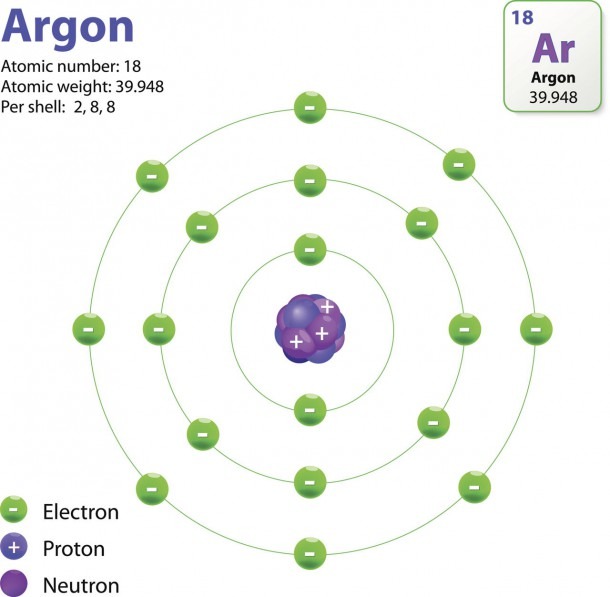
The Structure Of An Atom Explained With A Labeled Diagram Best Diagram Collection
Atomic or ionic charge = number of protons − number of electrons. An atom that gains one or more electrons will exhibit a negative charge and is called an anion. Positively charged atoms called cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. For example, a neutral sodium atom (Z = 11) has 11 electrons.

Atomic Structure Biochemistry
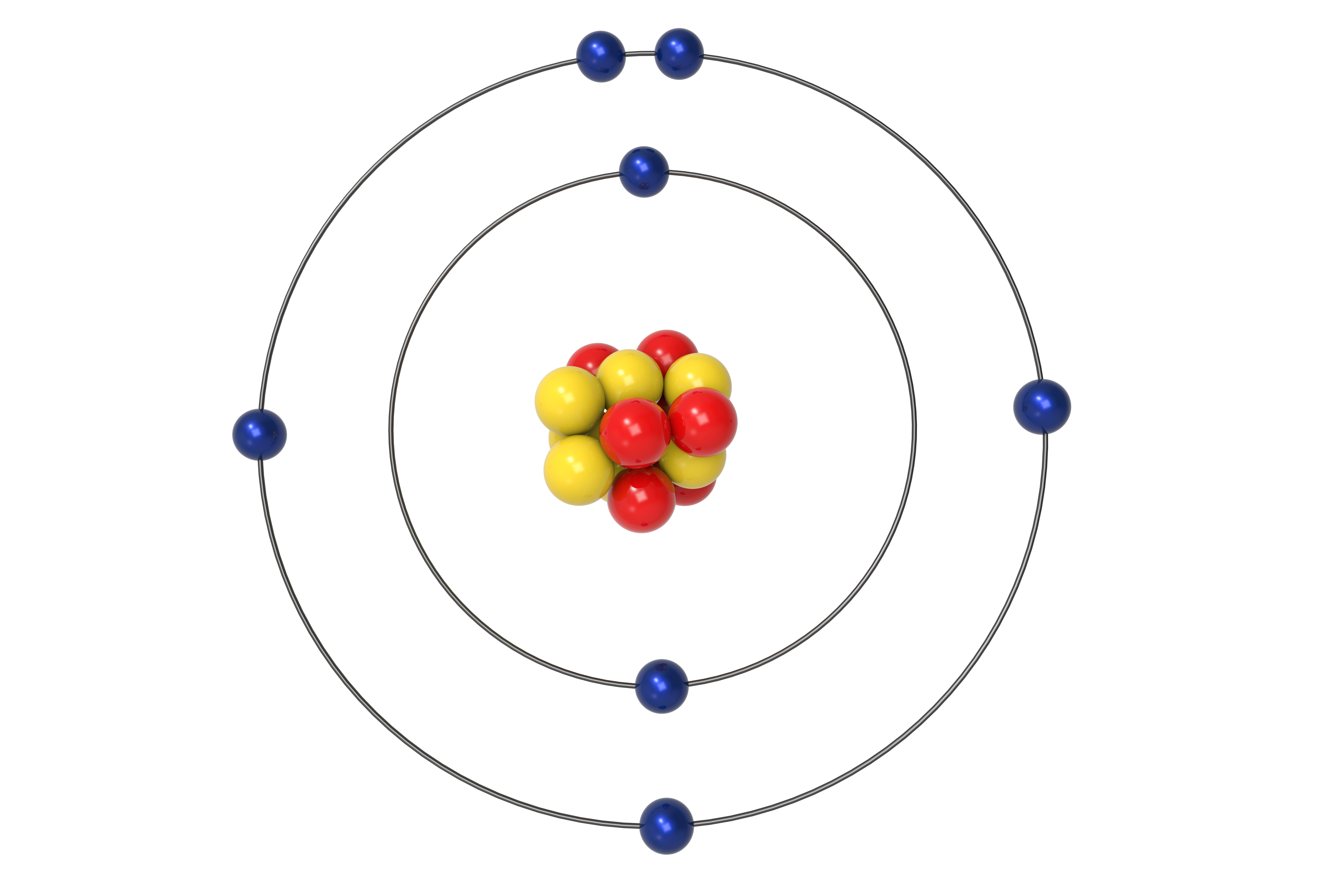
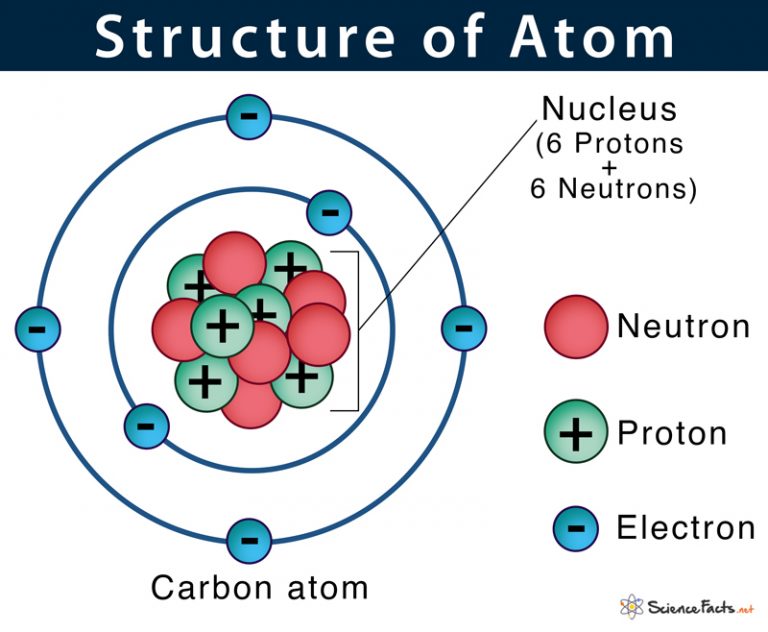
Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.

Learn the Parts of an Atom
An atom that gains one or more electrons will exhibit a negative charge and is called an anion. Positively charged atoms called cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. For example, a neutral sodium atom (Z = 11) has 11 electrons. If this atom loses one electron, it will become a cation with a 1+ charge (11 − 10 = 1+).

Structure of an atom universalxoler
2.3 Atomic Structure and Symbolism 2.3 Atomic Structure and Symbolism Highlights Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Write and interpret symbols that depict the atomic number, mass number, and charge of an atom or ion Define the atomic mass unit and average atomic mass

Atomic Structure Broad Learnings
The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n=3 to orbit n=2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV. (more)
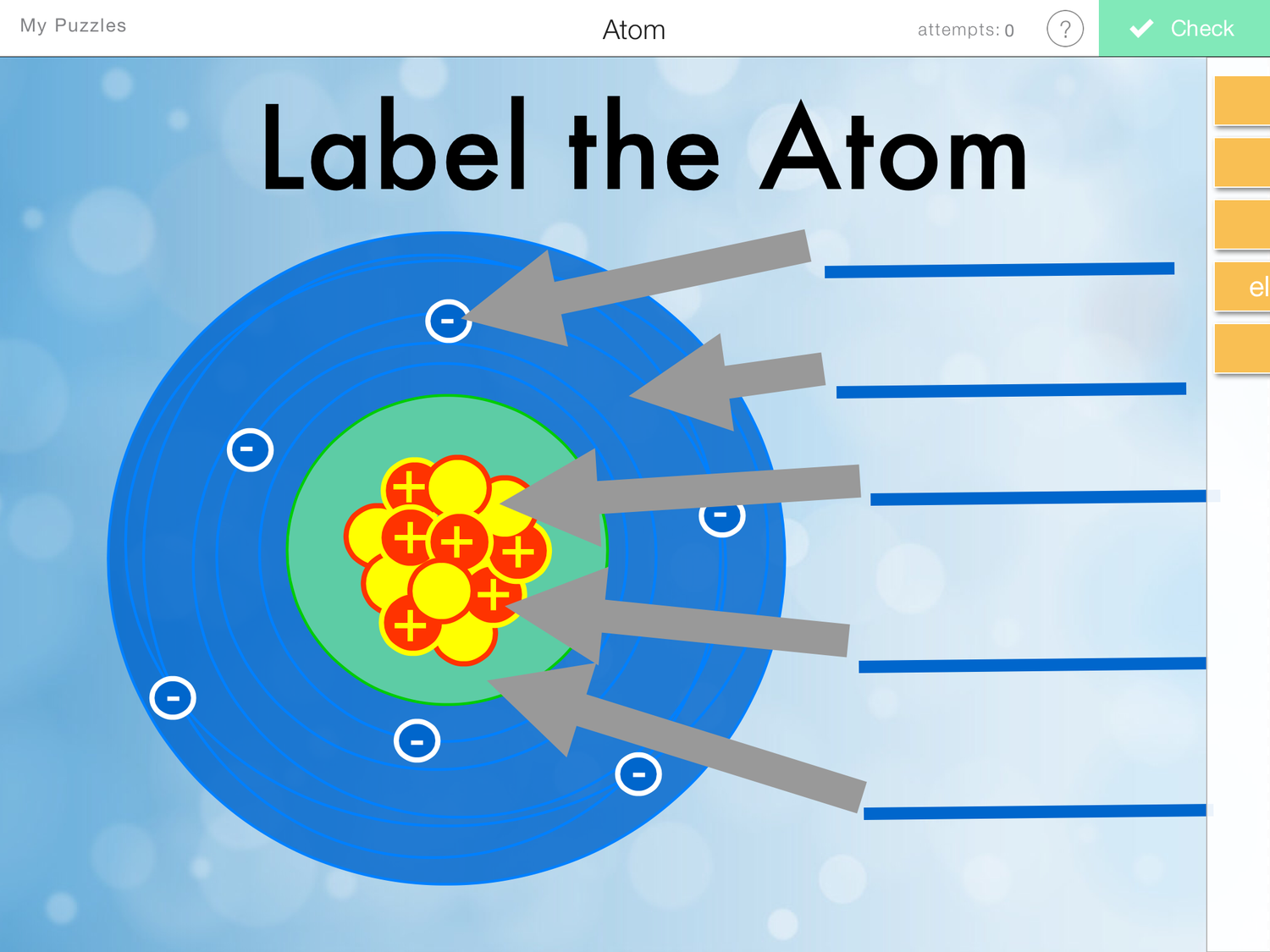
Label Parts of an Atom — Learning in Hand with Tony Vincent
Table 1. Properties of Subatomic Particles Charge (C) Mass (amu) Mass (g) −1.602 × 10 0.00091 × 10 The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is its atomic number (Z). This is the defining trait of an element: Its value determines the identity of the atom.
atom diagram to label
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of an element. Atoms are able to interact with each other through bonding, to form more complex substances, also known as molecules. These interactions determine the state of matter the atoms are in, as they can be found as solids, liquids, or gases.
Atomic Structure (GCSE) — the science sauce
Chemical Symbols. A chemical symbol is an abbreviation that we use to indicate an element or an atom of an element. For example, the symbol for mercury is Hg (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). We use the same symbol to indicate one atom of mercury (microscopic domain) or to label a container of many atoms of the element mercury (macroscopic domain).
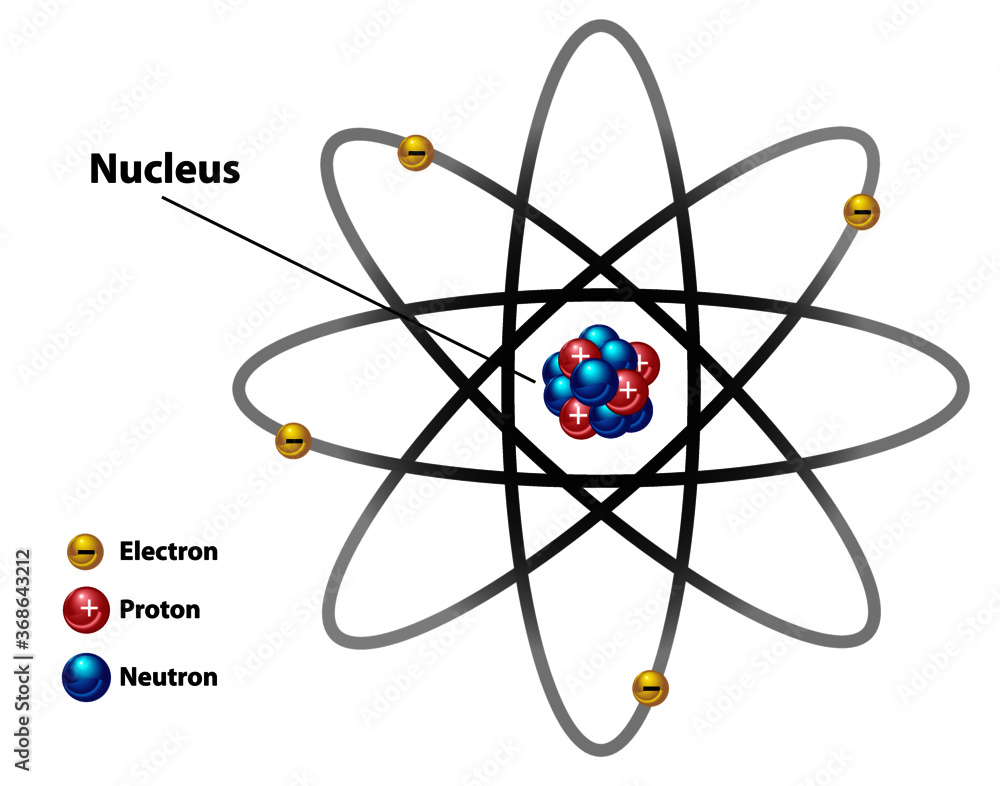
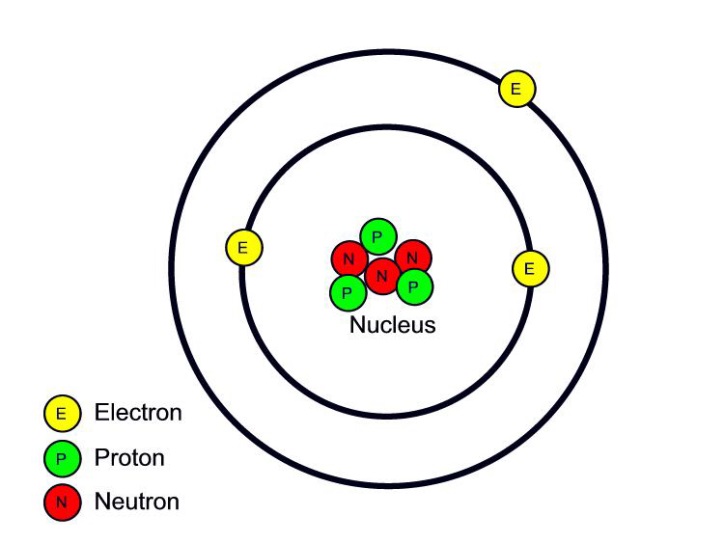
Atomic nucleus diagram labeled with electron, proton, and neutron. Stock Vector Adobe Stock
The periodic table By convention, elements are organized in the periodic table, a structure that captures important patterns in their behavior. Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns— groups —and rows— periods —that share certain properties.